Reflection at Plane and Spherical Surfaces
Reflection at Plane and Spherical Surfaces: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Reflection of Light, Laws of Reflection of Light, Average Speed of Image in Concave Mirror & Focal Plane of a Spherical Mirror etc.
Important Questions on Reflection at Plane and Spherical Surfaces
An object is placed in front of a convex mirror at a distance of 50 cm. A plane mirror is introduced covering the lower half of the convex mirror. If the distance between the object and the plane mirror is 30 cm, it is found that there is no gap between the images formed by the two mirrors. The radius of the convex mirror is:
In the figure shown, the image of a real object is formed at point I. AB is the principal axis of the mirror. The mirror must be:

The reflection surface of a plane mirror is vertical. A particle is projected in a vertical plane which is also perpendicular to the mirror. The initial velocity of the particle is 10 m/s and the angle of projection is 60o. The point of projection is at a distance 5 m from the mirror. The particle moves towards the mirror. Just before the particle touches the mirror the velocity of approach of the particle and its image is:
A large temple has a depression in one wall. On the floor plan, it appears as an indentation having a spherical shape of radius . A worshipper stands on the centreline of the depression, out from its deepest point, and whispers a prayer. Where is the sound concentrated after reflection from the black wall of the depression?
What happens to an image in a convex mirror?
An object is placed at from the concave mirror of focal length the nature of the image and magnification will be
What is the centre of curvature of spherical mirrors
A ray of light is incident towards a plane mirror at an angle of with the mirror surface.What will be the angle of reflection?
The principal focus of a spherical mirror lie midway between the pole and centre of curvature.
An object beyond the centre of curvature forms a real and _____ image between the focal point and the centre of curvature.
Centre of curvature of a concave mirror lies___________.
What will be the distance of the object,when a convex mirror produces an image of magnification ?The focal length of the mirror is .
According to the second law of reflection,angle of _____ is equal to the angle of reflection of light.
According to the second law of reflection, which angles will be equal?
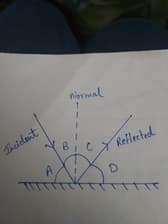
State the second law of reflection?
An object moving at a speed of towards a concave mirror of focal length is at a distance of . The average speed of the image is _____.
Define incident ray?
What can be the largest distance ( in centimetres) of an image of a real object from a convex mirror of radius of curvature ?
A virtual and same size image as object can be obtained by-
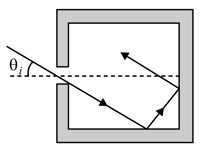
A monochromatic beam of light enters a square enclosure with mirrored interior surfaces at an angle of incidence (see the figure below). For some value(s) of , the beam is reflected by every mirrored wall (other than the one with opening) exactly once and exists the enclosure through the same hole. Which of the following statements about this beam is correct?